ps x
加上 “x” 选项(注意没有开头的”-“ 字符),告诉 ps 命令,展示所有进程,不管它们由什么 终端(如果有的话)控制。在 TTY 一栏中出现的 “?” ,表示没有控制终端.
l 多线程
s 一个信息头
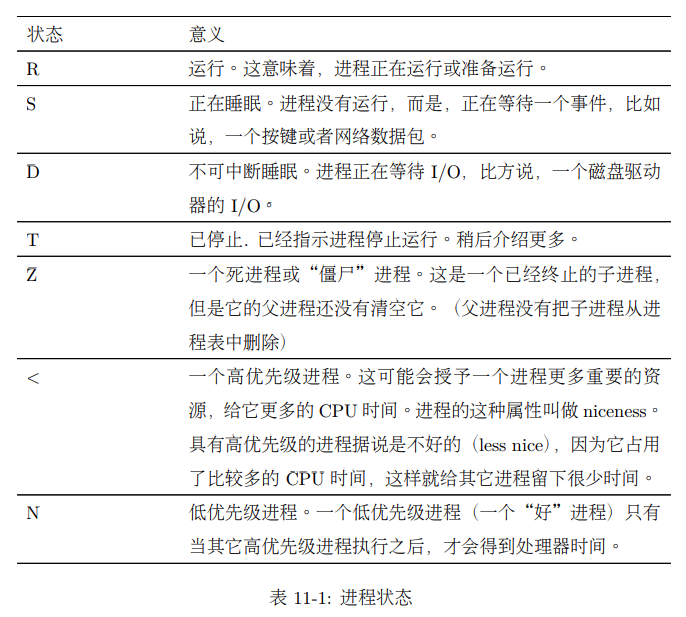
D 不可中断 uninterruptible sleep (usually IO)
R 运行 runnable (on run queue)
S 中断 sleeping
T 停止 traced or stopped
Z 僵死 a defunct (”zombie”) process
ps aux
这个选项组合,能够显示属于每个用户的进程信息
参数解释
a 显示所有进程
-A 显示所有进程
-e 等于“-A”
f 显示程序间的关系
USER:进程是属于哪一个人的;
PID: 进程ID;
%CPU:使用了多少 CPU 资源;
%MEM:使用了多少的 RAM ;
VSZ: 占用的虚拟内存大小kb
RSS:占用的物理内存的大小kb;
TTY:是否为登入者执行的进程?若为 tty1-tty6 则为本机登入者,若为 pts/?? 则为远程登入者执行的进程
STAT:状态
START:进程开始的日期;
TIME 运行的时间
COMMAND:该进程的内容
Instead of using awk to filter ps output, use the ps -o option to get what you want:
ps -e -o pid,comm
report current working directory of a process
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/unix_commands/pwdx.htm
pwdx `ps -ef | grep mysql | awk {'print$2'}`
实时查看进程
top 命令
htop 命令需要安装
apt-get install htop